Coronary Angiography
Angiography of the coronary arteries
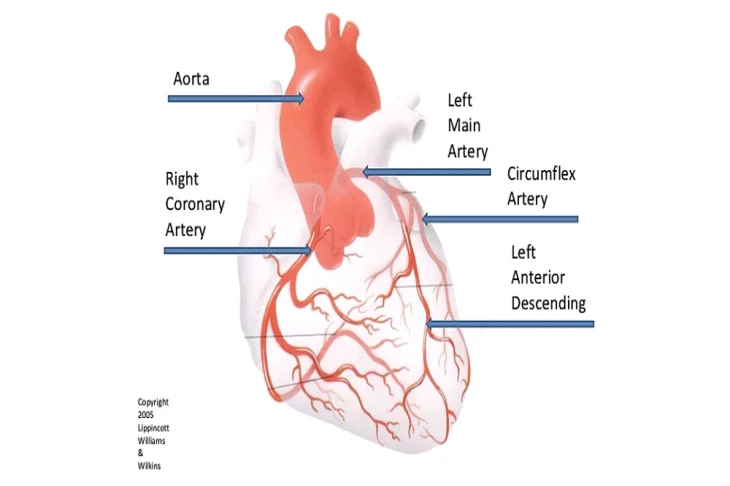
The heart pumps blood to every part of the body. The heart, on the other hand, need blood in order to function. Coronary arteries are three blood channels that supply blood to the heart. Coronary artery disease can be caused by a blockage in these arteries.
Coronary angiography is a medical imaging procedure that involves the use of X-ray equipment to scan the heart. This test produces an image of all three coronary arteries, as well as any constriction within them and their branches.
If you have any of the following symptoms, your doctor may consider a coronary angiography:
- A heart attack is an example of a sudden emergency
- Shortness of breath or chest discomfort (also known as angina).
- Stress test results were positive.
What is a coronary angiography and how does it work?
Coronary angiography is a specialized X-ray-based procedure used to produce clear images of the heart’s blood vessels. Since coronary arteries are not visible on a normal X-ray, a contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream to make these arteries visible.
This test is a vital part of coronary artery disease diagnosis, revealing the severity of the blockage and guiding the most suitable treatment – be it angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery.
Your doctor may recommend coronary angiography if you experience:
A sudden cardiac event, like a heart attack
Chest pain or angina, especially during exertion
Abnormal stress test results
Persistent shortness of breath
During a coronary angiography, what happens?
During a coronary angiography, a powerful X-ray machine called a cardiac catheterization machine is used in a specialized room known as the cardiac catheterization laboratory to carry out the procedure. This heart blockage test is performed under local anaesthesia and real-time X-ray guidance.
A thin, flexible catheter is inserted into a blood vessel either through the groin or wrist. The approach through the wrist is known as a radial angiography, which is now widely preferred due to its greater patient comfort and lower complication rate. This is a standard technique used in many top facilities offering angiography procedures in Bihar.
Once the catheter reaches the coronary arteries, a contrast dye is carefully injected. This dye makes the arteries visible on the X-ray screen and helps determine the exact location and severity of any blockages. After capturing the required images, the catheter is withdrawn, and the insertion site (groin or wrist) is dressed with a sterile bandage.
The entire procedure takes approximately 10 to 15 minutes. Afterward, you will be shifted back to your room where you’ll need to rest for a few hours for monitoring. You will also be advised to drink plenty of water to help flush the dye from your system through urine.
This minimally invasive procedure, guided by the best cardiologist in Patna, is a vital step toward diagnosing coronary artery disease and planning life-saving treatments such as angioplasty or stenting.
Are there any repercussions?
Angiography is a relatively risk-free procedure. A little bruise on your wrist or groyne is possible. Some persons may have an allergic reaction to the colour in rare situations.
What is the post-operative care like, and what are the risks?
- You have to spend many hours in the hospital ( sometimes a day). Any allergic reactions to the colour will be monitored.
- If the groyne was the site of the injury, you should avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for a few days.
- Your doctor will discuss the possibility of bleeding at the site as well as the precautions that must be taken.
What are the advantages of angiography of the coronary arteries?
One of the major advantages of coronary angiography is that it is a minimally invasive procedure that provides detailed and highly accurate imaging of the heart’s blood vessels. This advanced heart blockage test enables doctors to visualize any narrowing or obstruction in the arteries, making it an essential tool for coronary artery disease diagnosis.
Another significant benefit is that coronary angiography allows both diagnosis and treatment to be carried out in a single session. This eliminates the need for multiple procedures and reduces patient stress, hospital stay, and recovery time.
If additional procedures are necessary, such as angioplasty and stenting or bypass surgery, angiography acts as the first and most crucial step. It helps accurately locate problem areas and assess the severity o f blockages, allowing for a well-informed treatment plan to restore normal blood flow and reduce the risk of a future heart attack.
What are some of the drawbacks to coronary angiography?
Though we can usually accurately identify the extent of obstruction, we may underestimate or overestimate the extent of treatment in individuals with borderline lesions. This could have an impact on their overall treatment approach.
We can utilise a technique called Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) to precisely estimate the degree of the lesion and establish the treatment approach in such circumstances.